CryptoAuthentication in our Daily Lives – Efficient and Secure Management of Purchased Digital Credits
Feb 21, 2022
Article
It seems that each new day delivers yet another story of a data breach, large-scale hack, or electronic espionage of some sort. As much as networked devices have improved our lives with regard to daily efficiency, this large collection of interlinked data sources has also paved the way for a whole variety of criminal activity.
I mean, it’s just too tempting – knowing that interconnected collections of private data lie at the other end of an internet connection, though secured, obviously presents an alluring challenge for some people.
There are numerous ways to prevent unwanted visitors from viewing private data, with one of the most obvious solutions being that the data is simply disconnected from the internet. No connection to the data source means no access to the data – unless physically present at the data source, that is. The obvious downside to this is that there is no ability for external management, and the convenience of a networked device no longer applies.

Science fiction fans may recall that this non-networked strategy played an important role in the story line from the 2004 reboot of the series Battlestar Galactica. In the series, a few old Battlestar vessels were able to survive the Cylon attack because these old ships weren’t connected/networked with the rest of the fleet. For the sci-fi geeks: check out this humorous article by John Cox of NetworkWorld, as he recounts how a Cisco sales trainee attempted to sell an integrated computer network to the officers of the Galactica.
Despite the obvious benefits of networks, there are still applications where taking a non-networked approach does indeed make sense. And the security of these non-networked devices can be further enhanced by designing in a robust authentication system. Datakey CryptoAuthenticationTM memory tokens provide just such a solution.
Giving credit where credit is due
One possible application of secure data management in an offline environment is the management of digital credits – parking garage credits, in this case.
Imagine an environment where a city-owned parking ramp is located downtown near a host of bars, restaurants and small businesses whose customers park at the nearby parking ramp. These businesses entice customers by offering to validate (pay for) their parking in the ramp. Here’s how the parking credit management process works:
- The parking ramp uses a metering system that utilizes a secure portable memory device (like Datakey CryptoAuthentication memory tokens) to sell/transfer parking passes (in the form of digital credits) to nearby merchants using the ramp for their businesses.
- The merchant, in turn, has a device for validating parking tickets located in their place of business. The memory token is inserted into this device, loading the device with the number of validations (again, as digital credits) purchased. The security features of the CryptoAuthentication token ensure that the credits will only work with that merchant’s validation unit.
- During the business day, the merchants validate parking for customers or employees.
As parking tickets are validated, the credits on the memory token are decremented.
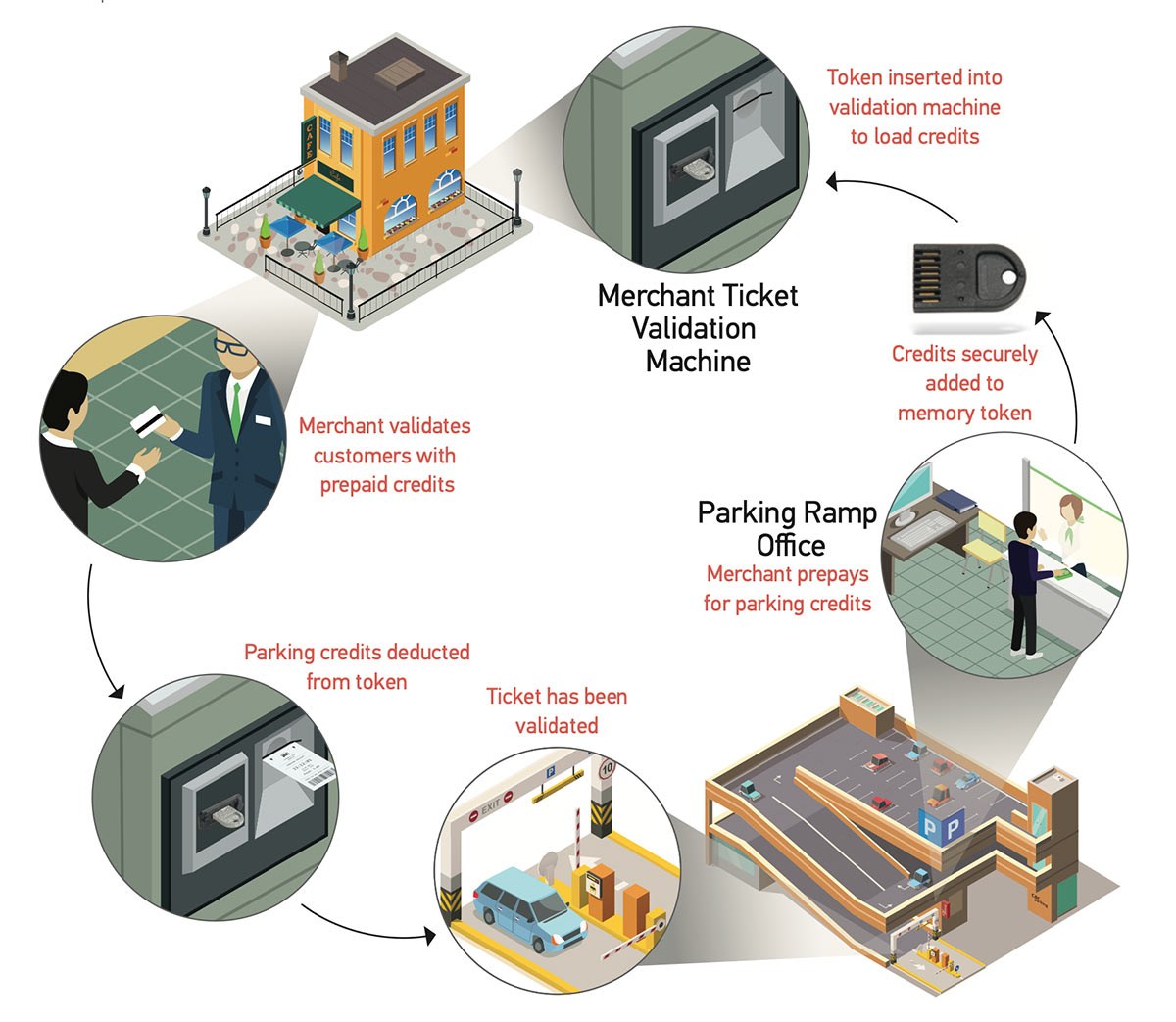
Using this credit-management process, the following are also options:
- Any unused credits can potentially be refunded to the merchant
- The memory token can be linked to a specific merchant, and/or the credits can possess an expiration date.
With this encrypted storage and transfer method, digital records are securely managed and transferred without the need to connect the validation machines to the internet. Additionally, the combination of the secure ramp-issued memory token and the validation machine it plugs into (that is physically secured inside the business’ brick-and-mortar structure) creates a controlled environment with safe data, and convenient records management.
A quick look behind the scenes
Technically, how are parking credits securely added and used? With our Datakey CryptoAuthentication memory tokens, the number and type of credits could be stored in one or more of the token’s secure memory slots.
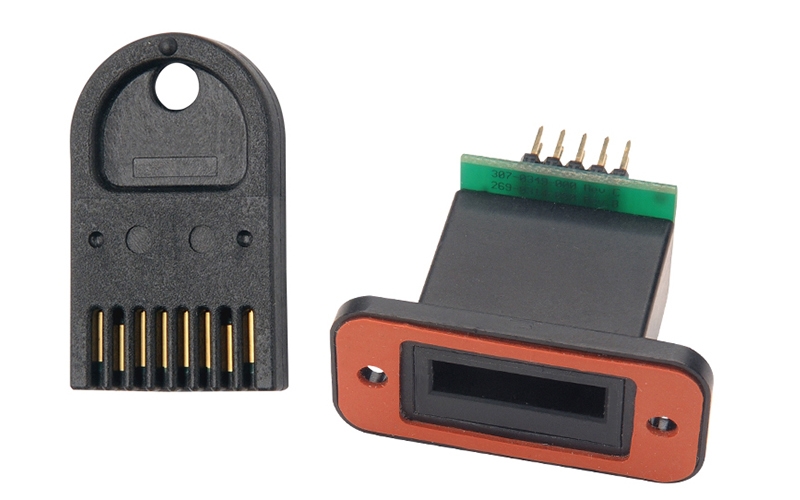

For example, let’s say that $500 of parking credits are stored in Slot 0. This slot, in turn, is protected by a read/write key stored in Slot 1. The read/write key, derived from the merchant’s PIN code, is used to access the memory token. When adding credits to the memory token, the new dollar amount is added to the Slot 0 value. Alternatively, using credits (at the point of validation inside the merchant’s business) subtracts the dollar amount from the current Slot 0 value. And, for added security, the token can be configured to handle interruptions from power loss or another event by utilizing Slot 2 for recording transactions before committing the changes to Slot 0, creating a simple transaction journal.
This is a very simplified explanation, of course, but hopefully it provides a rough outline of how to implement this type of application using a Datakey CryptoAuthentication memory token.
One of many possible applications
This application is just one of many potential uses of CryptoAuthentication memory tokens. While the name CryptoAuthentication may sound like something that would only be used with applications requiring the highest levels of security – if this technology is both affordable and accessible – why not implement it in as many applications as possible?
If secure memory technology is both affordable and accessible – why not implement it in as many applications as possible?
The rate at which cyber attacks are taking place, exposing private, personal information and costing institutions millions in repair and damage control, only seems to be growing. As enhanced methods of security continue to be devised and implemented, secure memory ICs (like Microchip’s ATSHA204A and ATECC608A ICs that are used in Datakey CryptoAuthentication memory tokens) are increasingly being integrated into the products prevalent in the environments in which we live.
Curious about other ways in which our CryptoAuthentication Memory Tokens can be used? Download our white paper (instant download, no registration required) highlighting several possible use cases for these tokens, including biometric access and inventory control applications, and get inspired as you think about your current and future projects and how they could benefit from using a high security portable memory device.
Want to see more potential uses for our CryptoAuthentication Memory Tokens?
Download the white paper